# Copyright (c) Meta Platforms, Inc. and affiliates. All rights reserved.
このチュートリアルでは、cameras、transforms、so3 APIを紹介します。
扱う問題は次のように定義されます。
外部パラメータ$\{g_1, ..., g_N | g_i \in SE(3)\}$を持つ$N$台のカメラの光学系と、ランダムに選択されたカメラのペア$(i, j)$の座標系間をマッピングする相対カメラ位置$\{g_{ij} | g_{ij}\in SE(3)\}$のセットが与えられた場合、相対カメラの動きと一致する絶対外部パラメータ$\{g_1, ..., g_N\}$を探します。
より正式には: $$ g_1, ..., g_N = {\arg \min}_{g_1, ..., g_N} \sum_{g_{ij}} d(g_{ij}, g_i^{-1} g_j), $$, ただし、$d(g_i, g_j)$はカメラ$g_i$と$g_j$の外部パラメータを比較する適切なメトリックです。
視覚的には、問題は次のように説明できます。下の図は、最適化の開始時の状況を示しています。真値カメラは紫色で、ランダムに初期化された推定カメラはオレンジ色でプロットされています: 
私たちの最適化は、相対カメラのペア間の不一致を最小限に抑えることで、推定(オレンジ)カメラを真値(紫)カメラに合わせようとしています。したがって、問題の解決策は次のようになります: 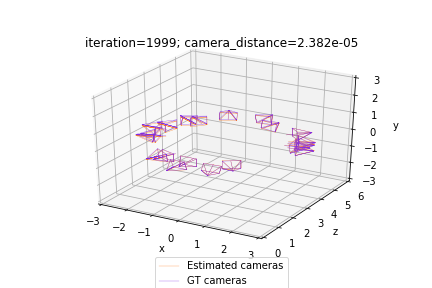
実際には、カメラの外部パラメータ$g_{ij}$と$g_i$は、外部パラメータ$g = (R, T); R \in SO(3); T \in \mathbb{R}^3$を定義する対応する回転行列と並進行列R_absoluteとT_absoluteで初期化されたSfMPerspectiveCamerasクラスのオブジェクトを使用して表されます。 R_absoluteが有効な回転行列であることを保証するために、回転の軸角度表現log_R_absoluteの指数マップ(so3_exp_mapで実装)を使用して表します。
この問題の解は、未知のグローバルな剛体変換$g_{glob} \in SE(3)$までしか復元できないことに注意してください。したがって、簡単にするために、最初のカメラ$g_0$の絶対外部パラメータがわかっていることを前提としています。 $g_0$を自明なカメラ$g_0 = (I, \vec{0})$として設定します。
torchとtorchvisionがインストールされていることを確認してください。 pytorch3dがインストールされていない場合は、次のセルを使用してインストールしてください。
import os
import sys
import torch
need_pytorch3d=False
try:
import pytorch3d
except ModuleNotFoundError:
need_pytorch3d=True
if need_pytorch3d:
if torch.__version__.startswith("2.2.") and sys.platform.startswith("linux"):
# We try to install PyTorch3D via a released wheel.
pyt_version_str=torch.__version__.split("+")[0].replace(".", "")
version_str="".join([
f"py3{sys.version_info.minor}_cu",
torch.version.cuda.replace(".",""),
f"_pyt{pyt_version_str}"
])
!pip install fvcore iopath
!pip install --no-index --no-cache-dir pytorch3d -f https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/pytorch3d/packaging/wheels/{version_str}/download.html
else:
# We try to install PyTorch3D from source.
!pip install 'git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d.git@stable'
# imports
import torch
from pytorch3d.transforms.so3 import (
so3_exp_map,
so3_relative_angle,
)
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import (
SfMPerspectiveCameras,
)
# add path for demo utils
import sys
import os
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(''))
# set for reproducibility
torch.manual_seed(42)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device("cuda:0")
else:
device = torch.device("cpu")
print("WARNING: CPU only, this will be slow!")
**Google Colab**を使用している場合は、カメラシーンをプロットするためのユーティリティファイルと、真値カメラの位置を取得します。
!wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d/main/docs/tutorials/utils/camera_visualization.py
from camera_visualization import plot_camera_scene
!mkdir data
!wget -P data https://raw.githubusercontent.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d/main/docs/tutorials/data/camera_graph.pth
または、**ローカル**で実行している場合は、次のセルのコメントを外して実行してください。
# from utils import plot_camera_scene
# load the SE3 graph of relative/absolute camera positions
camera_graph_file = './data/camera_graph.pth'
(R_absolute_gt, T_absolute_gt), \
(R_relative, T_relative), \
relative_edges = \
torch.load(camera_graph_file)
# create the relative cameras
cameras_relative = SfMPerspectiveCameras(
R = R_relative.to(device),
T = T_relative.to(device),
device = device,
)
# create the absolute ground truth cameras
cameras_absolute_gt = SfMPerspectiveCameras(
R = R_absolute_gt.to(device),
T = T_absolute_gt.to(device),
device = device,
)
# the number of absolute camera positions
N = R_absolute_gt.shape[0]
def calc_camera_distance(cam_1, cam_2):
"""
Calculates the divergence of a batch of pairs of cameras cam_1, cam_2.
The distance is composed of the cosine of the relative angle between
the rotation components of the camera extrinsics and the l2 distance
between the translation vectors.
"""
# rotation distance
R_distance = (1.-so3_relative_angle(cam_1.R, cam_2.R, cos_angle=True)).mean()
# translation distance
T_distance = ((cam_1.T - cam_2.T)**2).sum(1).mean()
# the final distance is the sum
return R_distance + T_distance
def get_relative_camera(cams, edges):
"""
For each pair of indices (i,j) in "edges" generate a camera
that maps from the coordinates of the camera cams[i] to
the coordinates of the camera cams[j]
"""
# first generate the world-to-view Transform3d objects of each
# camera pair (i, j) according to the edges argument
trans_i, trans_j = [
SfMPerspectiveCameras(
R = cams.R[edges[:, i]],
T = cams.T[edges[:, i]],
device = device,
).get_world_to_view_transform()
for i in (0, 1)
]
# compose the relative transformation as g_i^{-1} g_j
trans_rel = trans_i.inverse().compose(trans_j)
# generate a camera from the relative transform
matrix_rel = trans_rel.get_matrix()
cams_relative = SfMPerspectiveCameras(
R = matrix_rel[:, :3, :3],
T = matrix_rel[:, 3, :3],
device = device,
)
return cams_relative
最後に、絶対カメラの最適化を開始します。
モメンタム付きSGDを使用して、log_R_absoluteとT_absoluteを最適化します。
前述のように、`log_R_absolute`は絶対カメラの回転部分の軸角度表現です。 `log_R_absolute`に対応する3x3回転行列`R_absolute`は、次のようにして取得できます。
R_absolute = so3_exp_map(log_R_absolute)
# initialize the absolute log-rotations/translations with random entries
log_R_absolute_init = torch.randn(N, 3, dtype=torch.float32, device=device)
T_absolute_init = torch.randn(N, 3, dtype=torch.float32, device=device)
# furthermore, we know that the first camera is a trivial one
# (see the description above)
log_R_absolute_init[0, :] = 0.
T_absolute_init[0, :] = 0.
# instantiate a copy of the initialization of log_R / T
log_R_absolute = log_R_absolute_init.clone().detach()
log_R_absolute.requires_grad = True
T_absolute = T_absolute_init.clone().detach()
T_absolute.requires_grad = True
# the mask the specifies which cameras are going to be optimized
# (since we know the first camera is already correct,
# we only optimize over the 2nd-to-last cameras)
camera_mask = torch.ones(N, 1, dtype=torch.float32, device=device)
camera_mask[0] = 0.
# init the optimizer
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD([log_R_absolute, T_absolute], lr=.1, momentum=0.9)
# run the optimization
n_iter = 2000 # fix the number of iterations
for it in range(n_iter):
# re-init the optimizer gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# compute the absolute camera rotations as
# an exponential map of the logarithms (=axis-angles)
# of the absolute rotations
R_absolute = so3_exp_map(log_R_absolute * camera_mask)
# get the current absolute cameras
cameras_absolute = SfMPerspectiveCameras(
R = R_absolute,
T = T_absolute * camera_mask,
device = device,
)
# compute the relative cameras as a composition of the absolute cameras
cameras_relative_composed = \
get_relative_camera(cameras_absolute, relative_edges)
# compare the composed cameras with the ground truth relative cameras
# camera_distance corresponds to $d$ from the description
camera_distance = \
calc_camera_distance(cameras_relative_composed, cameras_relative)
# our loss function is the camera_distance
camera_distance.backward()
# apply the gradients
optimizer.step()
# plot and print status message
if it % 200==0 or it==n_iter-1:
status = 'iteration=%3d; camera_distance=%1.3e' % (it, camera_distance)
plot_camera_scene(cameras_absolute, cameras_absolute_gt, status)
print('Optimization finished.')
このチュートリアルでは、SfMカメラのバッチを初期化し、バンドル調整の損失関数を設定し、最適化ループを実行する方法を学びました。